
Are you experiencing peripheral edema as a side effect of taking amlodipine?
Don’t let this condition hinder your daily activities and quality of life. Our revolutionary treatment offers a reliable solution to mitigate peripheral edema caused by amlodipine.
Introducing our breakthrough therapy that targets and alleviates the discomfort caused by peripheral edema, ensuring you can resume your normal routine without worry.
Peripheral edema, which is the accumulation of fluid in the extremities, is a common side effect associated with amlodipine usage. It may cause swelling, puffiness, and discomfort, ultimately interfering with your daily life.
Our specialized treatment approach combines advanced medical expertise with the latest research to develop a personalized plan tailored to your unique needs. Our team of skilled professionals will conduct a thorough evaluation to gain a comprehensive understanding of your condition.
With our proven methods, we ensure efficient relief and long-lasting results. Our treatment aims to reduce the fluid retention and inflammation while improving blood circulation.
Regain control of your life today! Say goodbye to the discomfort and limitations caused by peripheral edema. Contact us now to schedule your consultation and start your journey towards positive, lasting recovery.
Understanding the causes
Amlodipine is a calcium channel blocker used to treat high blood pressure and chest pain (angina). However, one of the potential side effects of amlodipine is peripheral edema, which is the swelling of the lower limbs.
The exact mechanism by which amlodipine causes peripheral edema is not fully understood. However, it is thought to be related to the vasodilatory effects of the medication. Amlodipine relaxes the blood vessels, allowing for increased blood flow and reduced blood pressure. This relaxation of the blood vessels can also cause fluid to leak out into the surrounding tissues, leading to swelling.
In addition to its vasodilatory effects, amlodipine may also affect the balance of fluid and salt in the body. This can result in fluid retention, contributing to the development of peripheral edema.
It is important to note that not everyone who takes amlodipine will experience peripheral edema. The development of edema may depend on various factors, including the individual’s overall health, the dosage of amlodipine, and the presence of other medical conditions.
Potential risk factors for amlodipine-induced peripheral edema:
- Increasing age
- Female gender
- Use of higher doses of amlodipine
- Presence of heart failure
- History of peripheral edema or swelling
If you are taking amlodipine and experience swelling in your lower limbs, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider. They can evaluate your symptoms and determine the best course of action, which may include adjusting the dosage of amlodipine or exploring alternative treatment options.
The role of amlodipine in peripheral edema
Peripheral edema, or swelling in the lower extremities, is a common side effect of taking amlodipine. Amlodipine is a medication used to treat high blood pressure and certain types of chest pain.
When amlodipine is consumed, it works by relaxing and widening the blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more easily. However, one of the potential side effects of this medication is the accumulation of fluid in the tissues, leading to peripheral edema.
This swelling typically occurs in the lower legs, ankles, and feet, but can also affect the hands and arms. It is important to recognize the symptoms of peripheral edema, as it can be an indication that amlodipine is causing fluid retention in the body.
These symptoms may include:
- Swelling in the lower extremities
- Puffiness or bloating in the affected areas
- Tightness or discomfort in the affected areas
- Difficulty fitting into shoes or jewelry
If you are taking amlodipine and experiencing these symptoms, it is crucial to speak with your healthcare provider. They can determine if the peripheral edema is indeed related to the medication and recommend appropriate management strategies.
It is important to note that not everyone who takes amlodipine will experience peripheral edema. Certain factors, such as age, gender, and concurrent medical conditions, can increase the likelihood of developing this side effect.
Overall, understanding the role of amlodipine in peripheral edema is crucial in managing this side effect effectively. By recognizing the symptoms and seeking appropriate medical advice, individuals can take steps towards alleviating the discomfort and reducing the impact of peripheral edema on their daily lives.
Recognizing the symptoms
Peripheral edema, a common side effect of amlodipine, can present with various symptoms that are important to recognize in order to seek appropriate medical attention:
Swelling: One of the most noticeable symptoms of peripheral edema is swelling in the affected areas. This can occur in the hands, feet, ankles, and legs. The swelling may be mild or severe, depending on the individual.
Puffiness: Along with swelling, individuals may also experience puffiness in the affected areas. This may make the skin feel tight or stretched and can be visually apparent.
Tenderness: In some cases, individuals with peripheral edema may experience tenderness or discomfort in the swollen areas. This can make walking or standing for long periods of time painful.
Impaired movement: Peripheral edema can also affect mobility, as the swelling can make it difficult to move the affected limbs. This can lead to difficulties with daily activities and may impact quality of life.
Indentations: Pressing a finger into the affected area may leave an indentation that takes some time to disappear. This is known as pitting edema and is a common characteristic of peripheral edema.
Weight gain: Some individuals may notice an unexplained weight gain, which is often due to fluid accumulation caused by peripheral edema.
If you or a loved one is experiencing any of these symptoms while taking amlodipine, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance. Recognizing the symptoms early can help with effective management and potentially prevent further complications.
Identifying peripheral edema in patients
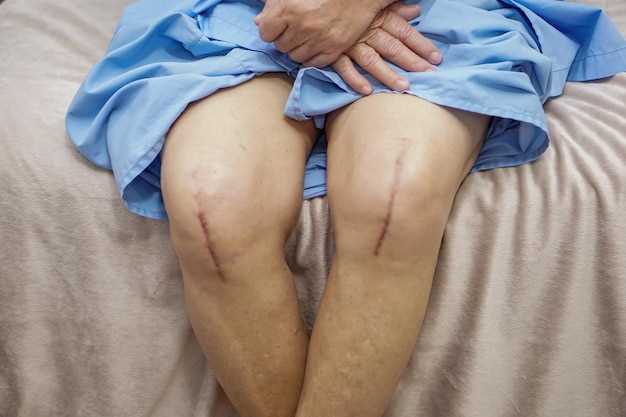
To effectively manage peripheral edema caused by amlodipine, it is essential to accurately identify the symptoms in patients. Peripheral edema is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the extremities, such as the legs, ankles, and feet. Patients experiencing peripheral edema may notice swelling, tightness, or a feeling of heaviness in these areas.
It is important for healthcare professionals to be observant and ask patients about any changes in their extremities. Patients should be asked if they have noticed any swelling or if their shoes or clothing have become tighter. Additionally, healthcare professionals should perform a physical examination to assess for any visible signs of peripheral edema.
Symptoms to look out for
Patients with peripheral edema may exhibit the following symptoms:
1. Swelling: The presence of swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet is a key indication of peripheral edema. The swelling may be localized or spread throughout the affected area.
2. Pitting edema: Pressure applied to the skin over the swollen area may result in a temporary indentation or “pit.” This is known as pitting edema and can be assessed by pressing a finger into the skin and observing the response.
3. Discomfort or pain: Patients may experience discomfort or pain in the swollen areas. This can range from a mild feeling of tightness to significant pain.
If any of these symptoms are present, it is important to consider the possibility of peripheral edema and explore the potential underlying causes.
Managing peripheral edema
Peripheral edema caused by amlodipine can be managed through various approaches. Here are some strategies that can help reduce swelling:
1. Adjusting the dosage: Consult with a healthcare professional to determine if the current dosage of amlodipine needs to be adjusted. Sometimes reducing the dose can help alleviate peripheral edema.
2. Elevating the legs: Elevating the legs can help improve circulation and reduce swelling. Lie down and raise your legs above the level of your heart for 15-20 minutes several times a day.
3. Wearing compression stockings: Compression stockings can help improve blood flow in the legs and reduce swelling. They apply pressure to the lower extremities, preventing fluid accumulation.
4. Incorporating exercise: Regular exercise can improve circulation and help reduce peripheral edema. Simple activities like walking or swimming can be beneficial. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any exercise routine.
5. Following a low-sodium diet: Consuming excessive amounts of sodium can contribute to fluid retention. To help manage peripheral edema, reduce your sodium intake by avoiding high-sodium foods such as processed snacks, canned soups, and fast food.
6. Avoiding prolonged sitting or standing: Sitting or standing for long periods can contribute to peripheral edema. Take breaks and move around to prevent fluid from pooling in your legs.
7. Using diuretics: In some cases, healthcare professionals may prescribe diuretics to help reduce fluid retention. These medications increase urine production, assisting in draining excess fluid from the body.
Remember, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your medication or treatment plan. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific situation.
Lifestyle changes for reducing swelling
Peripheral edema can be a common side effect of taking amlodipine. However, there are several lifestyle changes that can be implemented to help reduce swelling and discomfort caused by this condition.
1. Reduce sodium intake
High levels of sodium in the diet can contribute to fluid retention and worsen peripheral edema. It is important to limit the consumption of processed foods, fast food, and other high-sodium sources. Instead, opt for fresh, whole foods and season meals with herbs and spices rather than salt.
2. Increase water consumption

Drinking plenty of water can actually help flush out excess fluid in the body and reduce swelling. Staying hydrated is essential in managing peripheral edema. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day, and more if you are engaging in physical activity or in a hot climate.
3. Elevate your legs
When resting or sleeping, it can be beneficial to elevate your legs to encourage fluid drainage. Prop your legs up on a pillow or place a stool under them while sitting to help reduce swelling and relieve discomfort.
4. Avoid prolonged sitting or standing
Sitting or standing for long periods can worsen peripheral edema. Try to take breaks by walking around or stretching your legs throughout the day. If you have a desk job, consider using a standing desk or incorporating regular movement into your routine.
5. Engage in regular exercise
Physical activity can help improve circulation and reduce fluid retention. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as walking or swimming, most days of the week. Consult with your healthcare provider before starting any exercise program.
By implementing these lifestyle changes, you can effectively manage and reduce the swelling associated with peripheral edema caused by amlodipine. However, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and to discuss alternative treatment options.
Alternative treatment options
While amlodipine may be effective in treating certain conditions, such as high blood pressure or angina, it can also cause peripheral edema as a side effect. Fortunately, there are alternative treatment options available for individuals who experience edema while taking amlodipine.
1. Switching medications: One option is to switch to an alternative medication that does not have peripheral edema as a common side effect. This could involve consulting with your healthcare provider to determine which medication might be a suitable replacement for amlodipine.
2. Adjusting the dosage: Another option is to adjust the dosage of amlodipine. Sometimes, reducing the dosage can alleviate the symptoms of peripheral edema. However, it is essential to work closely with your healthcare provider when making any changes to the prescribed dosage.
3. Combination therapy: In some cases, a combination of medications may be necessary to address both the underlying condition and the peripheral edema caused by amlodipine. Your healthcare provider can help determine if combination therapy is appropriate for you.
4. Natural remedies: Certain natural remedies may help reduce swelling and alleviate the symptoms of peripheral edema. These can include herbal supplements, dietary changes, and exercises that promote circulation. However, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider before trying any natural remedies to ensure they are safe and suitable for your specific situation.
5. Lifestyle modifications: Making certain lifestyle modifications can also help manage peripheral edema. These can include reducing sodium intake, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, elevating the legs when resting, wearing compression stockings, and avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing.
Remember, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider before making any changes to your medication or treatment plan. They can provide personalized advice and guidance based on your specific condition and medical history.
Exploring alternative medications for amlodipine-induced edema
While amlodipine is an effective medication for treating various cardiovascular conditions, it can sometimes cause peripheral edema as a side effect. If you experience this issue, it’s important to consult with your doctor to explore alternative medications that may have a lower risk of causing edema.
1. Diuretics
Diuretics, also known as water pills, are often prescribed to reduce edema by increasing the removal of excess fluid from the body. They work by promoting urine production and reducing fluid retention. Your doctor may consider prescribing diuretics as an alternative to amlodipine to help manage the edema.
2. Calcium Channel Blockers
Calcium channel blockers (CCBs) are a class of medications that work similarly to amlodipine by relaxing blood vessels and improving blood flow. However, not all CCBs have the same side effects profile. Your doctor may recommend a different CCB that is less likely to cause peripheral edema.
| Medication | Side Effects |
|---|---|
| Amlodipine | Peripheral edema |
| Nifedipine | Less commonly associated with edema |
| Verapamil | Less commonly associated with edema |
By considering an alternative CCB, you may be able to find a medication that effectively manages your cardiovascular condition without the unwanted side effect of peripheral edema.
It’s crucial to have an open conversation with your doctor about any concerns or issues you experience with amlodipine. Together, you can explore alternative medications and find the best solution for your individual needs.
