
Amlodipine is a medication used to treat high blood pressure and chest pain (angina). However, recent studies have shown a potential link between amlodipine and fatty liver disease.
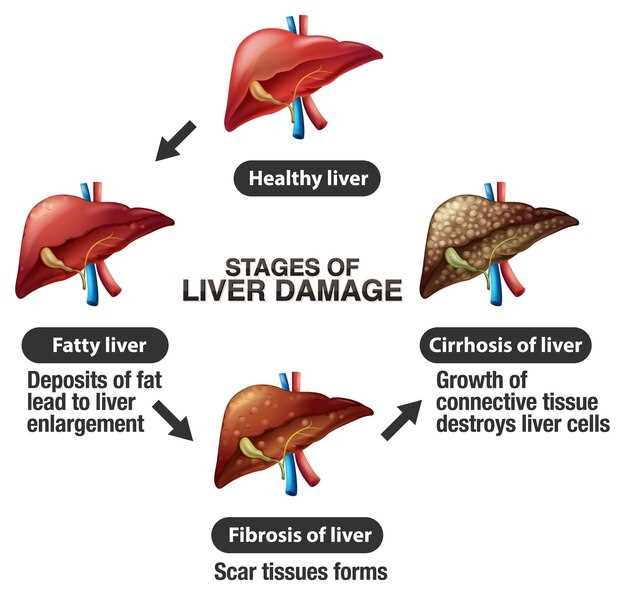
Fatty liver disease is a condition in which fat builds up in the liver, leading to inflammation and damage. This can result in liver dysfunction and other serious health problems.
While more research is needed, it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with amlodipine and fatty liver disease. If you are currently taking amlodipine, it is recommended to speak with your doctor about any concerns or symptoms you may be experiencing.
Remember, your liver plays a crucial role in maintaining your overall health, so it is important to take any potential risks seriously and seek medical advice if needed.
Impact of Fatty Liver
When it comes to maintaining a healthy liver, it is crucial to understand the impact that fatty liver can have on our overall well-being. Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fat in the liver cells.
Fatty liver can be caused by various factors, including obesity, high cholesterol, and diabetes. If left untreated, it can lead to more severe liver diseases such as cirrhosis and liver failure, which can significantly impact our quality of life.
The Connection Between Fatty Liver and Amlodipine
Now, you might be wondering what the connection between fatty liver and Amlodipine is. Amlodipine is a widely prescribed medication used to treat high blood pressure and certain types of heart disease. While Amlodipine has been proven to be effective in managing these conditions, it is important to consider its compatibility with fatty liver.
In individuals with fatty liver disease, the liver is already compromised, and certain medications can further exacerbate the condition. Therefore, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new medications, including Amlodipine.
The Compatibility of Amlodipine with Fatty Liver
Studies have shown that Amlodipine has minimal effects on fatty liver disease. In fact, it may even have some positive effects on liver health. Amlodipine has been found to improve liver function and reduce inflammation in individuals with fatty liver disease.
However, it is crucial to note that everyone’s health condition is unique, and the impact of Amlodipine on fatty liver may vary from person to person. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or pharmacist, to determine the best treatment option for your specific situation.
Recommendations for Amlodipine Usage
If you have been diagnosed with fatty liver disease and are considering taking Amlodipine, here are some recommendations to keep in mind:
- Consult with a healthcare professional before starting Amlodipine to ensure it is suitable for your specific condition.
- Follow the prescribed dosage and medication instructions provided by your healthcare professional.
- Monitor your liver function regularly through blood tests to assess the impact of Amlodipine on your fatty liver disease.
- Adopt a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, to support liver health.
By following these recommendations and consulting with your healthcare professional, you can make informed decisions about the use of Amlodipine in managing your fatty liver disease.
Impact of Fatty Liver
A fatty liver is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver cells. This condition is often caused by excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, insulin resistance, and high levels of triglycerides in the blood.
When the liver becomes infiltrated with fat, it can lead to inflammation and liver damage. It can also impair the liver’s ability to function properly, including its ability to metabolize drugs.
The impact of fatty liver on the use of Amlodipine, a commonly prescribed medication for high blood pressure, is an important consideration.
1. Metabolism and Absorption
The presence of fatty liver can affect the metabolism and absorption of Amlodipine. Studies have shown that individuals with fatty liver may have altered drug metabolism, which can result in higher blood levels of the medication. This means that the effects of Amlodipine may be prolonged or intensified in patients with fatty liver.
2. Drug Clearance
In individuals with fatty liver, the clearance of Amlodipine from the body can be reduced. This is because the liver, which is responsible for metabolizing and eliminating drugs from the body, may not function optimally in individuals with fatty liver. As a result, the medication may accumulate in the body, leading to potential side effects and adverse reactions.
Therefore, it is important for individuals with fatty liver to be closely monitored when taking Amlodipine. The dosage may need to be adjusted or an alternative medication may be considered.
- Regular liver function tests should be conducted to ensure that the liver is functioning properly and to monitor any potential liver damage.
- If severe liver disease is present, the use of Amlodipine may need to be avoided altogether.
- Individuals with fatty liver should follow a healthy lifestyle, including weight loss if necessary, to improve liver function and reduce the risk of complications.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting or discontinuing any medication, including Amlodipine, especially in individuals with fatty liver.
Compatibility of Amlodipine with Fatty Liver
Amlodipine, a commonly prescribed medication for high blood pressure, has been a subject of interest regarding its compatibility with fatty liver. Fatty liver, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells. It is often associated with obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol levels.
Studies have shown that Amlodipine does not directly affect fatty liver or contribute to its development. However, it is essential for individuals with fatty liver to closely monitor their liver function while taking Amlodipine. The medication itself is unlikely to worsen fatty liver, but it is essential to consider other aspects, such as overall health and lifestyle, in managing both conditions.
| Benefits of Amlodipine | Impact of Fatty Liver |
|---|---|
|
|
Given the potential risks associated with fatty liver, it is crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to manage both high blood pressure and fatty liver. Regular monitoring of liver function, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and following a balanced diet are essential steps in effectively managing both conditions. Your healthcare provider can also provide guidance on adjusting the dosage of Amlodipine, if necessary, based on your liver function.
In conclusion, while Amlodipine does not directly impact fatty liver, individuals with fatty liver should be vigilant about monitoring their liver function. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance on managing both conditions and to ensure the compatibility of Amlodipine with any pre-existing liver conditions.
Recommendations for Amlodipine Usage
1. Take the prescribed dosage of Amlodipine as directed by your healthcare professional. Do not exceed or reduce the recommended dose without consulting your doctor.
2. Amlodipine should be taken once a day, preferably at the same time each day. This will help you remember to take your medication regularly.
3. It is important to continue taking Amlodipine even if you feel well. Stopping the medication suddenly may cause your blood pressure to spike, which can be dangerous.
4. Store Amlodipine tablets in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Do not keep the medication in the bathroom or near the kitchen sink where it can be exposed to humidity and heat.
5. If you miss a dose of Amlodipine, take it as soon as you remember. However, if it is close to the time of your next dose, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular dosing schedule. Do not take a double dose to make up for the missed one.
6. Be sure to inform your doctor about any other medications you are currently taking, as some drugs may interact with Amlodipine and affect its effectiveness or increase the risk of side effects.
7. If you experience any unusual or severe side effects while taking Amlodipine, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or irregular heartbeat, seek medical attention immediately.
8. Always attend regular check-ups with your doctor to monitor your blood pressure and overall health. Your doctor may need to adjust your dosage or recommend alternative treatments if necessary.
9. It is essential to follow a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques, to complement the effects of Amlodipine and improve your overall cardiovascular health.
10. Inform your healthcare professional if you have a history of liver problems or if you develop any symptoms of liver disease while taking Amlodipine, such as abdominal pain, dark urine, or yellowing of the skin and eyes.
11. Finally, do not share your Amlodipine medication with others, even if they have similar symptoms or conditions. Amlodipine is specifically prescribed to you based on your specific medical needs and should not be used by anyone else without medical supervision.
